Description
Pseudogout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes joint inflammation due to the body depositing calcium pyrophosphate crystals in the joint and soft tissues. Pseudogout is also called calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD). Gout is a more commonly known, similar type of inflammatory arthritis.
Although in gout, monosodium urate crystals are deposited in the joint and soft tissues. In each of these conditions, the crystals and the body’s reaction to them within the joint can lead to joint damage.
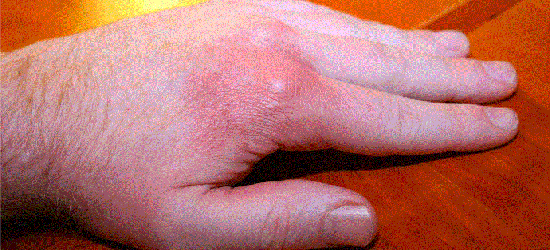
Inflammatory arthritis is different from degenerative arthritis, which includes conditions such as osteoarthritis. In pseudogout, patients will experience symptoms similar to gout arthritis with episodes of swelling, pain and redness of joints (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Acute pseudogout episode with a swollen, red and painful finger
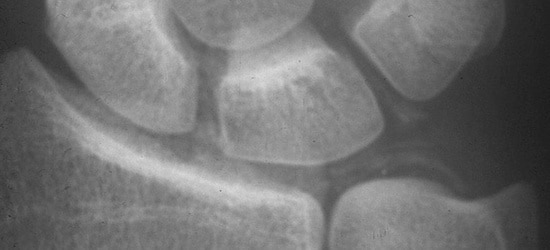
Figure 2: Pseudogout in the wrist often has deposits like the ones seen here
CauseshELLO
The reason why some bodies deposit crystals and cause pseudogout is not known. There may be a hereditary predisposition to the process. There are certain risk factors associated with the disorder. Pseudogout occurs more often in men over 60 years of age and in people with a history of thyroid disorders, kidney failure, and a disorder of calcium or iron metabolism. Pseudogout may develop related to hypothyroidism or hyperparathyroidism.
Sudden attacks of pseudogout are likely related to release of the calcium pyrophosphate crystals within the joint fluid causing the symptoms of severe pain, swelling and redness.
Signs and Symptoms
Pseudogout often affects the wrists and hands but can happen in any joint. Patients may notice white deposits (Figure 2) underneath the skin due to a collection of calcium pyrophosphate crystals, but this is not common. Sudden episodes of joint pain are also associated with redness and swelling of the affected joints. The episodes of pain, swelling and redness can be so severe that they appear similar to an infection within the joint.
Doctor Examination
The diagnosis of pseudogout is often made after a history, physical examination and x-rays. Your doctor will ask about your pain, medical history and examine your joints. The x-rays of an involved joint may show evidence of calcification within the cartilage surfaces and soft tissue of the extremity. The most definitive way to diagnose pseudogout is to remove fluid from a joint where it is present with a needle so the fluid can be analyzed.
Treatment
Initial treatment of a painful arthritic episode includes rest and ice to the painful joint. Other treatment options may include:
- A splint, which can improve pain by limiting the motion of the involved joint while it is inflamed
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or naproxen
- Steroids (given by mouth) or an injection to help decrease the inflammation
Your doctor may have other medication options as well. Surgical treatment is occasionally performed to relieve the symptoms of a painful flare by cleaning out the joint crystals and calcification.